Among the 113 active cannabinoids present in the cannabis (Cannabis sativa L.) plant, cannabidiol (CBD) and Tetrahydro Cannabinol (THC) are being discussed and researched extensively in the scientific community.
While both the Cannabinoids have medicinal benefits, THC causes euphoria or intoxication in most people, which has limited its use in therapeutic treatments. On the other hand, CBD does not induce any intoxicating effects and is known to have various medicinal benefits. Due to this, CBD has emerged as a promising candidate for the treatment of several CNS conditions, such as neuropathic pain, chronic inflammation, and epilepsy. In addition, CBD has been found to be useful in the treatment of cancer-induced pain and childhood seizures. In fact, a drug called Sativex developed by GW Pharmaceuticals – containing CBD and THC has gained approval across Asia and Europe for treating spasticity and cancer pain. Beyond this, CBD has shown potential in the treatment of substance abuse.
The increasing research on the usage of cannabis in medical interventions demands for enhanced purification and detection assays for cannabinoids. Further, as the FDA is not currently regulating Cannabis production and there is no external quality control over the cannabis producing farms, researchers need to have access to highly pure, research-grade THC-free CBD to carry out their research safely and reliably. This has made it essential to design an optimal extraction process for CBD for maximum recovery of the pure cannabinoid.
Two methods- namely High-performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) and Centrifugal Partition Chromatography (CPC) are the most commonly used techniques for cannabis purification. Although HPLC is used industry-wide, Centrifugal Partition Chromatography (CPC) is emerging as a relatively cost-effective alternative. Research has shown that CPC has a similar yield to HPLC, and it also helps in generating a highly pure product. If you are considering cannabis testing, you need to be aware of the working principle of both of these techniques in order to select the right method for your specific needs.
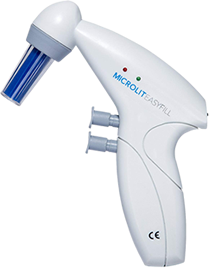
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
HPLC can be used for compound identification (analytical HPLC), as well as sample extraction (preparative HPLC) from crude mixtures. In an HPLC process, a mobile phase is used to carry the sample through a stationary phase. This results in the separation of individual components on the basis of particle size or any other physical characteristic. After leaving the column, the samples produce a signal (peak), and can be collected as fractions.
Advantages of using HPLC:
- Silica-resin packed HPLC columns are highly suitable for extracting cannabinoids from a crude cannabis mixture, and are known to exhibit excellent purity and yield.
- Moreover, in an HPLC process, the purification controls are highly optimized, eliminating the need for any troubleshooting protocols.
Disadvantages of using HPLC:
Although HPLC is an industry-wide accepted technique for cannabis testing, there are many disadvantages associated with it, including:
- The cost of stationary columns used in the assay is very high.
- HPLC setup needs large reagent volumes for mobilization of pure fractions, leading to high costs and complexities in large scale studies.
- HPLC requires greater run times, further adding to the cost.
- HPLC columns need to be tailored according to the size of the compound to be extracted.
- HPLC columns often need to be replaced repeatedly, especially for cannabinoid extraction which is generally sticky in nature.
Centrifugal Partition Chromatography (CPC)
As mentioned earlier, CPC is relatively a cost-effective alternative to HPLC. It is a silica-free liquid chromatography technique, in which the stationary liquid phase and the immiscible mobile phase are merged to create a two phase system. The stationary phase is held together by the centrifugal force inside the column. In order to extract cannabinoids, the crude mixture and mobile phase are injected and pumped through the column, which are then separated on the basis of their partition coefficient. Further, the composition of mobile and stationary phases is varied in order to selectively extract the cannabinoids and obtain an ideal partition coefficient.
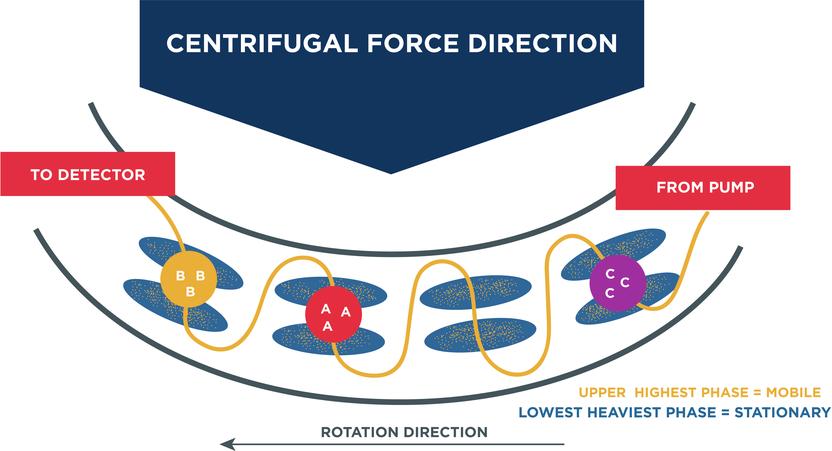
Advantages of using CPC:
- The run times of CPC are relatively less than HPLC
- The assay requires lesser amount of solvent, accompanied by a high recovery percentage.
- Although CPC columns can be costly, they can be used and re-used for several types of samples, such as complex synthetic and natural mixtures.
Disadvantages of using CPC:
CPC is relatively a new technique, therefore, it needs to be optimized carefully before it can be used in large-scale and high priced projects.
Summing Up
Cannabis testing and purification has gained substantial importance in recent times, given its increasing application in the medical field. This has increased the demand for a cost-effective purification method, which can produce high yield of purified cannabinoids. While HPLC is a commonly used extraction method, the efficiency, cost-effectiveness, scalability and yield makes CPC a more suitable choice for cannabinoid researchers. It is crucial to be aware of the pros and cons related to both the techniques, in order to make an informed choice for their cannabis purification needs.






 9681
9681