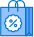
Titration is a method commonly used in a laboratory that uses a solution of one known concentration to analyze and determine the known concentration of another solution. Typically, the titrant (known solution) is added with a burette into a known amount of analyte (unknown solution) until the reaction is complete. Often, an indicator is used to indicate the endpoint, usually the end of the reaction.





 5115
5115