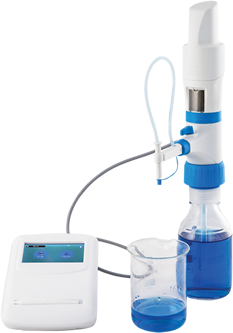
Efficient liquid handling is a cornerstone of successful laboratory operations, especially in fields like molecular biology, diagnostics, and drug development. The right tools can drastically improve accuracy, throughput, and overall productivity. Among these tools, multichannel pipettes have emerged as game-changers for labs handling large sample volumes. But how do you know if your lab needs one? This blog explores the multichannel, its key advantages, and how they can revolutionize your workflow.
Introduction: What is a Multichannel Pipette?
A multichannel pipette is designed to simultaneously transfer liquid into multiple wells or containers. Instead of handling one sample at a time, a multichannel pipette allows users to dispense or aspirate liquid across 8, 12, or even 16 channels in a single operation.
Types of Multichannel Pipettes
Multichannel pipettes are available in various designs to suit different lab needs.
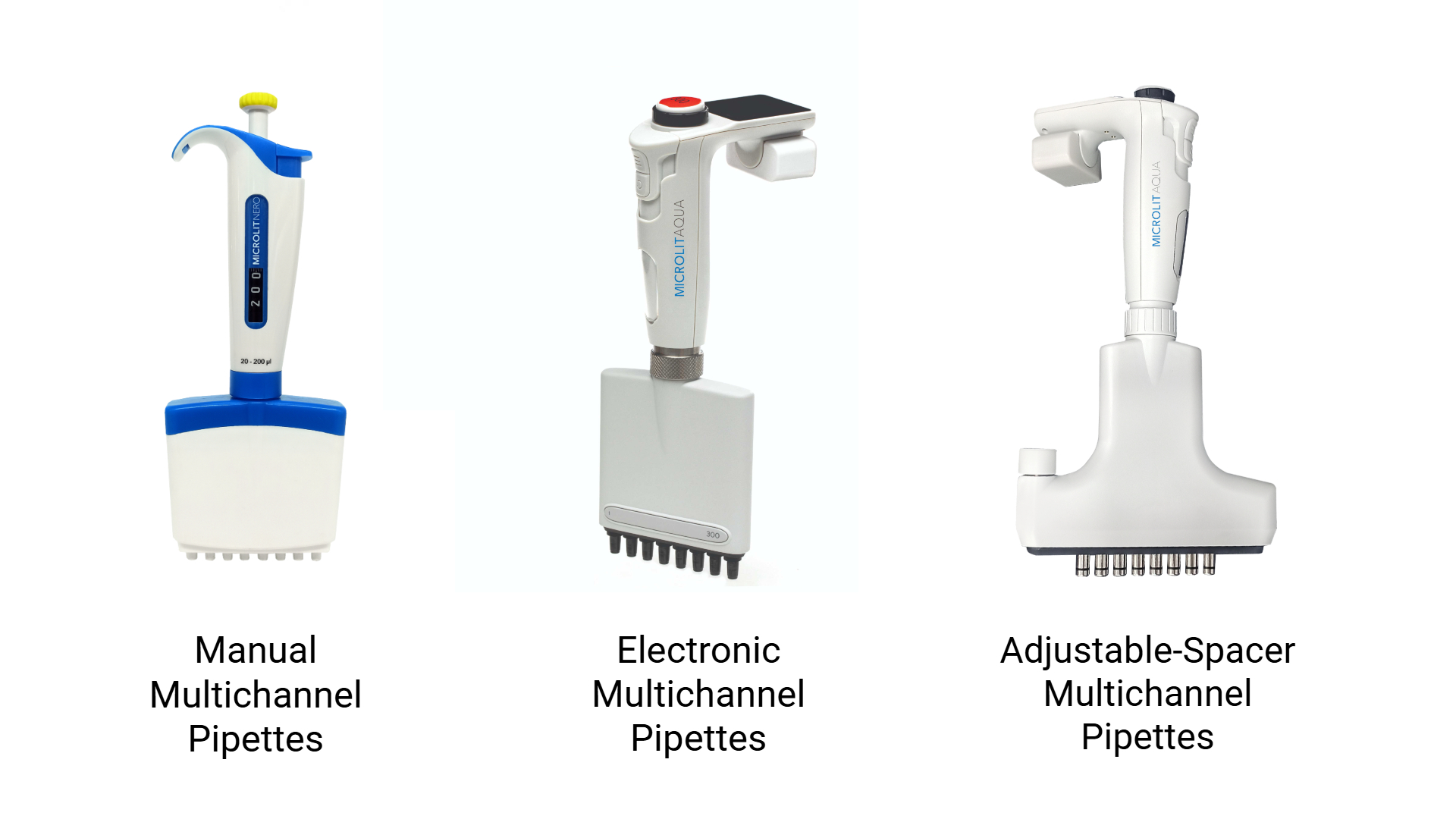

- Manual Multichannel Pipettes
These pipettes require manual operation but are ergonomically designed to reduce strain. They are cost-effective and suitable for routine tasks.
- Electronic Multichannel Pipettes
Electronic models offer automated pipetting functions, reducing user effort and increasing precision. Advanced features like programmable volume settings and adjustable speeds make them ideal for complex workflows.
- Adjustable-Spacer Multichannel Pipettes
These pipettes allow the spacing between channels to be adjusted, making them versatile for transferring liquids between plates, tubes, or reservoirs with varying formats.
Key Features of Multichannel Pipettes
- Multiple ChannelsTypically available in 8 or 12 channels to match microplate formats (96-well or 384-well plates).
- Consistent DispensingEnsures uniform liquid transfer across all channels, reducing errors.
- Adjustable Tip SpacingOffers flexibility for transferring liquids between different well or tube formats.
Differences Between Multichannel and Single-Channel Pipettes
| Feature | Multichannel Pipette | Single-Channel Pipette |
| Number of Channels | Multiple (8, 12, or 16) channels | Single channel |
| Design Purpose | Transfers liquid into multiple wells simultaneously | Transfers liquid into one well at a time |
| Throughput | High throughput, ideal for repetitive tasks | Low throughput, suitable for individual handling |
| Speed | Faster due to simultaneous dispensing | Slower as it handles one sample at a time |
| Applications | Best for ELISA, PCR, and filling multi-well plates | Suitable for sample preparation and small volumes |
| Accuracy | Consistent across multiple channels but may vary slightly due to tip alignment | Highly accurate for single transfers |
| Ease of Use | Requires practice to align tips and dispense evenly | Simple and easy to use, minimal training required |
| Physical Effort | Ergonomically reduces strain in repetitive tasks | Can cause fatigue in repetitive tasks |
| Cost | More expensive due to the complex design | More affordable |
| Tip Usage | Requires multiple tips per operation | Requires one tip per operation |
| Ideal Plate Formats | Designed for 96-well and 384-well plates | Flexible for tubes, plates, or containers |
| Learning Curve | Moderate, with a need to master tip alignment | Minimal |
| Time Efficiency | Saves time significantly in multi-sample workflows | Time-consuming for repetitive tasks |
| Maintenance | Slightly more complex due to multiple channels | Straightforward due to simple design |
Advantages of Using Multichannel Pipettes
- Enhanced Throughput
Multichannel pipettes are indispensable for labs working with high-throughput applications. Tasks like filling microplates for ELISA, PCR, or cell culture can be completed in a fraction of the time compared to single-sample pipetting.
For example:
-
-
- Filling a 96-well plate with a single-channel pipette could take over 20 minutes.
- A multichannel pipette can reduce this task to just 2-3 minutes.
-
- Time Efficiency
Time saved in repetitive pipetting tasks translates directly into increased productivity. This is especially critical in workflows where multiple plates need to be processed in a day, such as drug discovery or high-throughput screening (HTS).
- Consistency and Accuracy
With proper calibration, multichannel pipettes provide uniform dispensing across all channels. This is crucial in applications where precise liquid volumes are essential to maintain experimental validity, such as serial dilutions or reagent addition in assays.
- Reduced User Fatigue
Manually pipetting into hundreds of wells using a single-channel pipette can be tedious and strain-inducing. Multichannel pipettes reduce the physical effort required, allowing lab personnel to work more comfortably and efficiently over extended periods.
- Minimized Human Error
Repetitive pipetting increases the likelihood of mistakes, such as skipping wells or inconsistent volumes. Multichannel pipettes streamline the process, ensuring even distribution of liquid and reducing variability between wells.
Applications of Multichannel Pipettes
Multichannel pipettes are especially beneficial for laboratories that routinely handle high throughput workflows. Common applications include:
- ELISA Assays
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA) involve repetitive dispensing of reagents across multiple wells. Multichannel pipettes simplify this process, ensuring uniform reagent addition and reducing variability in assay results.
- PCR and qPCR Preparation
Preparing PCR or qPCR plates requires precision and speed to avoid the degradation of reagents like enzymes or primers. Multichannel pipettes make it easy to add master mixes or samples efficiently across all wells.
- Serial Dilutions
Performing serial dilutions across microplates becomes significantly faster with a multichannel pipette. This is particularly useful in titration experiments or when determining minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) in microbiology studies.
- Cell Culture
In cell biology labs, seeding cells or adding growth media to plates is a routine task. Multichannel pipettes help maintain sterility and consistency across wells, promoting reliable experimental outcomes.
- Drug Screening and High-Throughput Screening (HTS)
Pharmaceutical and biotechnology labs use multichannel pipettes extensively for compound screening. Handling large sample volumes quickly and accurately is essential to ensure reproducible results.
A multichannel pipette can be a transformative tool for labs aiming to improve efficiency and consistency in liquid handling. The benefits are significant, especially for high-throughput applications, from reducing workload to minimizing errors.
If your lab frequently works with microplates or handles repetitive pipetting tasks, investing in a multichannel pipette is a smart decision. Not only will it save time, but it will also enhance the reliability of your results, ultimately contributing to the success of your experiments.
Microlit is a trusted name in high-precision liquid handling instruments, offering solutions that elevate accuracy, efficiency, and reliability in laboratory workflows. Known for its innovative engineering and ergonomic designs, Microlit’s product portfolio includes micropipettes, bottle-top dispensers, burettes, and advanced electronic liquid handling systems. To know more about Microlit products or its pipette range, please contact at info-usa@microlit.com or visit the website www.microlit.us.






 1096
1096