Cell culture is the removal of cells either from plants or animals and cultivated in an artificial environment under controlled conditions for biological research. It is an invaluable tool to understand physiological processes, mechanisms of underlying diseases, effects of drugs and toxic compounds, and drug screening and development. Cell culture is also used in vaccine research, protein therapeutics, and cancer research. It is a meticulous process and one that requires a lot of diligence, skill, and experience.
Cell culture processes and procedures
The processes and procedures of cell culture depend on the cell type and application. There are two techniques of obtaining cells, from the cell bank or by isolating cells from tissue.
From Cell Bank
The cell culture procedure followed for cells obtained from the cell bank include:
Thawing – the cryopreserved cells are thawed in a 37°C water bath or a melting apparatus. Before the ice almost melts, the medium is added to dilute the cryoprotectant liquid, the cells are precipitated. The supernatant is removed, and a fresh medium preheated to 37°C is added. The cells are then resuspended using a pipette.
Cell Seeding – the desired cell seeding density is achieved by measuring cell numbers and dilute the cell suspension accordingly.
Cell Observation – after cell seeding, the cells are observed in the vessel with an optical microscope to check the viable cells, cells are evenly distributed in the vessel, presence of foreign objects, and check cell morphology. The cell culture vessel is then placed in a humidified CO2 incubator at 37°C to start culturing.
From Donor Tissue
When cells obtained from tissue, the procedure followed is:
Cell Isolation – the cells are isolated from the tissue using two methods, explant culture, and enzymatic method. In the enzymatic method, proteolytic enzyme solution is used, which is then diluted and then proceed to steps of cell seeding and cell observation to prepare cell culture.
Basic equipment and reagents required in this application
There are several equipment and reagents used in cell culture, these include:
Laminar airflow, incubator, pipettes, burettes, bottle top dispensers, inverted microscope, water bath, centrifuge, cell culture vessels, consumables, and many more.
The reagents are complete medium, buffered solutions, detaching agents, cryoprotective agents, and distilled water.
Benefits of using liquid handling instruments in cell culture
Cell culture involves meticulous liquid handling, which can be a tiresome and time-consuming procedure if not done properly. The slightest error can result in contamination and damage the cell culture. The liquid handling instruments satisfy the prerequisites as they are designed to improve liquid handling accuracy and precision, increase efficiency and avoid any chance of contamination.
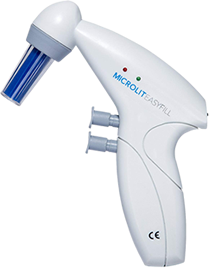
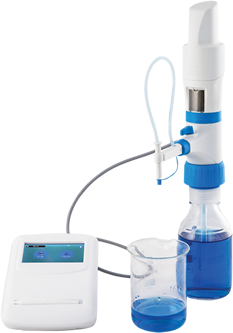
The liquid handling instruments used in the cell culture process are pipettes, burettes, and bottle top dispensers. Serological pipettes are used to resuspend the cells. The burettes are used to dispense the accurate amount of reagent to detach, buffer, or isolate the cells. Bottle top dispensers are used in the sample preparation process to provide convenient dispensing of reagents. They significantly enhance productivity and prevent hazards.
Conclusion
The role of liquid handling equipment is essential in cell culture as they provide accuracy, precision and convenient sample preparation. The equipment minimizes contamination, reduces inconsistencies in sample yield, and helps prepare uniform quantities.
Microlit is a trusted manufacturer in providing high-quality liquid handling instruments for cell culture as well as other applications. To learn more about our products, please email us at info-usa@microlit.com.






 6275
6275